What is Relay ? types of relay also Parts of relay

Relay Definition:
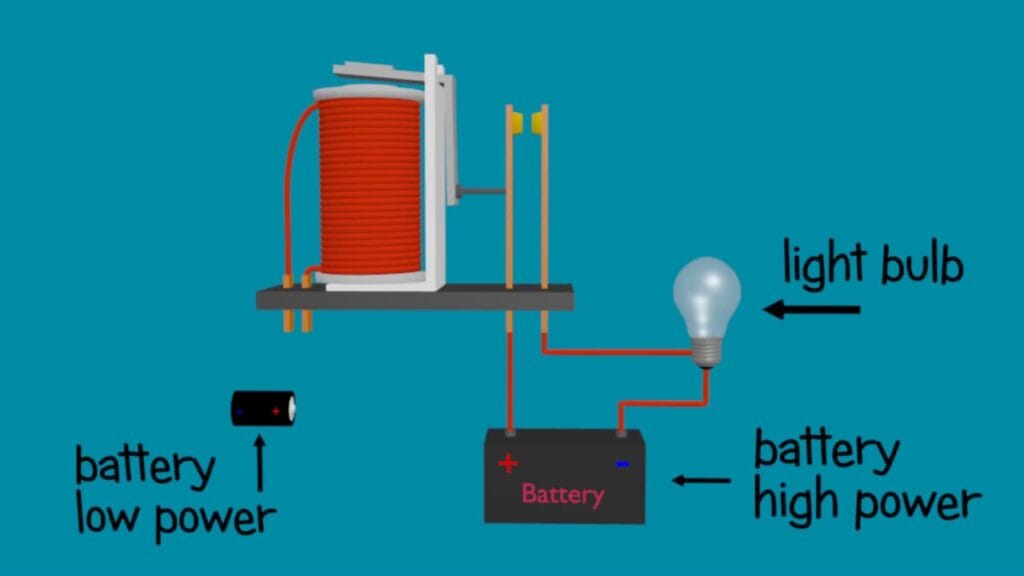
A relay can be defined as a switch (open and close circuits electromechanically). Switches are generally used to close or open the circuit manually .Relay is also a switch that connects or disconnects two circuits. But instead of manual operation a relay is applied with electrical signal, which in turn connects or disconnects another circuit without any human involvement.

Working Principle Of Relay:
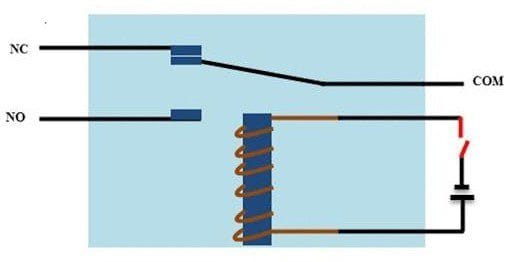
(i) Relay works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
(ii) When the electromagnet is applied with some current it induces a magnetic field around it.
(iii)Above image shows working of the relay .A switch is used to apply DC current to the load.
(iv)In the relay Copper coil and the iron core acts as electromagnet.
(v) When the coil is applied with DC current it starts attracting the contact as shown. This is called energizing of relay.
(vi)When the supply is removed it retrieves back to the original position. This is called De energizing of relay.
Parts Of Relay:
- Electromagnet: An Electromagnet plays a major role in the working of a relay. It is a metal which doesn’t have magnetic property but it can be converted into a magnet with the help of an electrical signal. We know that when current passes through the conductor it acquires the properties of a magnet. So, when a metal is winded with a copper wire and driven by the sufficient power supply, that metal can act as a magnet and can attract the metals within its range. Relay can be operated using either AC or DC. In case of AC relays, for every current zero position, the relay coil gets demagnetized and hence there would be a chance of continues breaking of the circuit. So, AC relays are constructed with special mechanism such that continues magnetism is provided in order to avoid above problem.
(b) Movable Armature: Movable armature is a simple metal piece which is balanced on a pivot or a stand. It helps in making or breaking the connection with the contacts connected to it.
(d) Contact: These are the conductors that exist within the device and are connected to the terminals.
(e) Yoke: It is a small metal piece fixed on a core in order to attract and hold the armature when the coil is energized.
Types Of Relay:
Generally, there are four types of relays as follows:
- Single Pole Double Throw Relay: A Single Pole Double Throw Relay is a relay that has one input and two outputs. Internally, it is wired so it is connected as shown below:

b. Single Pole Double Throw Relay: A Single Pole Double Throw Relay is a relay that has one input and two outputs. Internally, it is wired so it is connected as shown below:

Being that it has 2 outputs, it is more dynamic than a single throw relay. It can connect to 2 different outputs, so it can switch a circuit in between any 1 or 2 states, such as ready mode- pause mode, etc.
c. Double Pole Single Throw Relay: A Double Pole Single Throw (DPST) Relay is a relay that has 2 inputs and 2 outputs. Internally, it is wired so it is connected as shown below:
Each of the inputs can connect to one output. A DPST relay is constructed internally as if they are 2 separate SPST relays connected together. So a DPST is really just 2 separate SPST relays .
d. Double Pole Double Throw Relay : A Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT) is a relay that has 2 inputs and 4 outputs. Internally, it is wired so it is connected as shown below:

The 2 input stages can each connect to 2 different outputs, allowing for 4 different output modes. A circuit with a DPDT allows for the most dynamic and versatile of outputs being that it can switch between these different modes.
